Fighting Urinary Tract Infections with Cranberry Juice
It has been observed by scientists that with eight hours of drinking cranberry juice, it can prevent bacteria from forming inside the urinary tract. UTIs are a type infection caused by bacteria entering and growing in your urinary tract system. Your urinary system involves both the kidneys, two ureters, your bladder, and the urethra. The most common type of infection is caused by E-coli bacteria, although some of these bacteria are thought to come from fecal matter.
 The bacteria responsible for more than %95 of urinary tract infections are a pathogenic strain of the same E. coli bacteria found in the lower intestine. The problematic strain of E. coli carries tiny, arm-like appendages called fimbriae that anchor the bacteria to the surfaces of the urinary tract’s cells. If not for these fimbriae, the flow of urine would simply wash the bacteria away. However, once they’re securely latched onto the urinary tract walls, they quickly start reproducing.
The bacteria responsible for more than %95 of urinary tract infections are a pathogenic strain of the same E. coli bacteria found in the lower intestine. The problematic strain of E. coli carries tiny, arm-like appendages called fimbriae that anchor the bacteria to the surfaces of the urinary tract’s cells. If not for these fimbriae, the flow of urine would simply wash the bacteria away. However, once they’re securely latched onto the urinary tract walls, they quickly start reproducing.
It was found that cranberries contain molecules known as proanthocyanidins and flavonols which are thought to be responsible for preventing E-coli with Fimbriae to adhere to your cell walls. While this will help you flush out the bacteria, it doesn’t affect the growth rate of E-coli, though it can protect against some bacteria. Bacterial movement is a key mechanism for infection to spread, as bugs literally swim to the urinary tract and escape the body’s immune system response.
 Research has found that cranberry juice alters and increases certain thermodynamic properties of bacteria in the urinary tract, including the amount of energy they have to use up before they can attach to the tissue. This creates an energy barrier that they can’t overcome, and prevent them from latching on. If the bacteria can’t stick to the walls of the urinary tract, then they can be flushed out by the urine.
Research has found that cranberry juice alters and increases certain thermodynamic properties of bacteria in the urinary tract, including the amount of energy they have to use up before they can attach to the tissue. This creates an energy barrier that they can’t overcome, and prevent them from latching on. If the bacteria can’t stick to the walls of the urinary tract, then they can be flushed out by the urine.
Studies show that cranberry juice seems more effective at preventing future bacterial infections than treating an existing one. The first thing to keep in mind is that treating and preventing urinary tract infections are two very different subjects. Cranberries are filled with antioxidants and have long been considered a very valuable boost to our overall health. In addition to these antioxidants, cranberries contain hippuronic acid. This compound has been shown to make it much more difficult for the bacteria which causes urinary tract infections, to attach to the bladder wall because this acid works to acidify the urine. This lowers the risk of getting a UTI in some cases. There are doctors that believe that once you have a UTI, cranberries in any form will do little to help treat it, and can actually make urination even more painful.
If you do want to try it, make sure that you are drinking 100% pure and natural cranberry juice because most of the sweetened versions with added sugar do not contain hippuronic acid and may aggravate your UTI even more.

 Subscribe Now
Subscribe Now

 Drink a lot of water. Water is the best and the safest method to get rid of the infection. It dilutes the urine and empties out the bladder. There are two kinds of urine, one is dark, concentrated and painful to pass while the other one is lighter, easy to pass and does not burn. One should avoid drinking tea, coffee or soda as they can further irritate the bladder.
Drink a lot of water. Water is the best and the safest method to get rid of the infection. It dilutes the urine and empties out the bladder. There are two kinds of urine, one is dark, concentrated and painful to pass while the other one is lighter, easy to pass and does not burn. One should avoid drinking tea, coffee or soda as they can further irritate the bladder. Although
Although 
 The cause of an overactive bladder is unknown. Risk factors include obesity, caffeine, and
The cause of an overactive bladder is unknown. Risk factors include obesity, caffeine, and  A Urinary Tract Infection (UTI), also known as acute cystitis or bladder infection, is an infection that affects part of the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a bladder infection and when it affects the upper urinary tract it is known as a kidney infection. Symptoms from a lower urinary tract include painful urination and either frequent urination, the urge to urinate or both. The symptoms of pyelonephritis include fever and flank pain in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI.
A Urinary Tract Infection (UTI), also known as acute cystitis or bladder infection, is an infection that affects part of the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a bladder infection and when it affects the upper urinary tract it is known as a kidney infection. Symptoms from a lower urinary tract include painful urination and either frequent urination, the urge to urinate or both. The symptoms of pyelonephritis include fever and flank pain in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI.




 Urinary Tract Infections are caused when the bladder is not completely emptied or something irritates the urinary tract. UTIs are the second most common type of infection in humans and The National Kidney & Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse (NKUDIC) reports that UTIs account for over 8 million doctor visits annually.
Urinary Tract Infections are caused when the bladder is not completely emptied or something irritates the urinary tract. UTIs are the second most common type of infection in humans and The National Kidney & Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse (NKUDIC) reports that UTIs account for over 8 million doctor visits annually.
 The reason why urinary infections occur in cats and dogs is because of E.coli which is a particular kind of bacteria and it stays near the urethra and enters it when the pet’s immunity is compromised and then reaches the urinary tract and the bladder. The problems that are caused because of this bacteria are kidney stones, stress, bladder abnormalities,
The reason why urinary infections occur in cats and dogs is because of E.coli which is a particular kind of bacteria and it stays near the urethra and enters it when the pet’s immunity is compromised and then reaches the urinary tract and the bladder. The problems that are caused because of this bacteria are kidney stones, stress, bladder abnormalities,  A lower urinary bladder infection can result in licking around the urinary opening, bad smelling or cloudy urine, and difficulty while urinating. Other symptoms include blood in the cat’s or dog’s urine, if there are accidents in the house or there is urine leakage. When it comes to cats, they will cry out or scream when they try to urinate. In cases of upper urinary tract infection, cats and dogs may show a lack of interest in eating, weight loss and vomiting. Serious symptoms can show lethargy, fever and abdomen tenderness. It is necessary that when such symptoms are present in your pet that you take them to a veterinary immediately. Even if there are no symptoms present, it is necessary to take your pet to a vet on a regular basis.
A lower urinary bladder infection can result in licking around the urinary opening, bad smelling or cloudy urine, and difficulty while urinating. Other symptoms include blood in the cat’s or dog’s urine, if there are accidents in the house or there is urine leakage. When it comes to cats, they will cry out or scream when they try to urinate. In cases of upper urinary tract infection, cats and dogs may show a lack of interest in eating, weight loss and vomiting. Serious symptoms can show lethargy, fever and abdomen tenderness. It is necessary that when such symptoms are present in your pet that you take them to a veterinary immediately. Even if there are no symptoms present, it is necessary to take your pet to a vet on a regular basis.
 Anything that obstructs the normal flow of urine from the kidneys and the bladder to the outside of the body can increase the risk of a UTI. Things like kidney stones, an enlarged prostate gland in men, urinary catheters, and genetic abnormalities in the urinary tract can interfere with urine flow. Women have more UTIs than men, and as women get older, the risk gets higher. There are a few different approaches to this as some believe that since women have a shorter urethra, bacteria can enter the urinary tract and travel up to the bladder more quickly. Others think that it is triggered by sexual intercourse or an increase of the amount of bacteria in the vagina. Since the opening of the urethra is very close to the vagina, bacteria have a short distance to travel. Pregnancy can also increase the risk, since all the extra weight puts pressure on the bladder and kidneys, making it easier for bacteria to set up shop. Last but not least, women who use diaphragms or spermicides for birth control are more likely to get a UTI.
Anything that obstructs the normal flow of urine from the kidneys and the bladder to the outside of the body can increase the risk of a UTI. Things like kidney stones, an enlarged prostate gland in men, urinary catheters, and genetic abnormalities in the urinary tract can interfere with urine flow. Women have more UTIs than men, and as women get older, the risk gets higher. There are a few different approaches to this as some believe that since women have a shorter urethra, bacteria can enter the urinary tract and travel up to the bladder more quickly. Others think that it is triggered by sexual intercourse or an increase of the amount of bacteria in the vagina. Since the opening of the urethra is very close to the vagina, bacteria have a short distance to travel. Pregnancy can also increase the risk, since all the extra weight puts pressure on the bladder and kidneys, making it easier for bacteria to set up shop. Last but not least, women who use diaphragms or spermicides for birth control are more likely to get a UTI. Good hygiene and simple self-help methods are critical for maintaining optimal urinary health. Both men and women should wash themselves regularly, and keep the vaginal or penile areas clean after urinating or after a bowel movement.
Good hygiene and simple self-help methods are critical for maintaining optimal urinary health. Both men and women should wash themselves regularly, and keep the vaginal or penile areas clean after urinating or after a bowel movement.
 Cystitis is a bacterial infection causes your bladder to become inflamed. It happens when bacteria enter your bladder through your urethra, the tube that carries urine out of your body. Cystitis is a common type of lower urinary tract infection.
Cystitis is a bacterial infection causes your bladder to become inflamed. It happens when bacteria enter your bladder through your urethra, the tube that carries urine out of your body. Cystitis is a common type of lower urinary tract infection.
 Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids daily. Water can help flush bacteria from your system, prevent new infections and perhaps even flush the beginnings of an infection from your system.
Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids daily. Water can help flush bacteria from your system, prevent new infections and perhaps even flush the beginnings of an infection from your system.

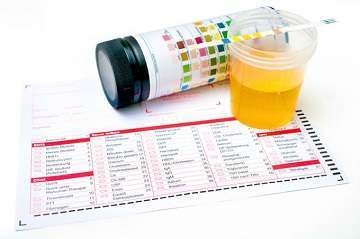 Another way is to dip test strips in the urine and these will show if a urine infection is present. However, these are usually not enough to be sure, unless the child has had infections before. The test strip results may be normal even if a child has an infection. Collecting clean urine for this test from young children can be difficult and a special bag may be used. Sometimes the urine is collected in other ways, such as using a catheter. If a urine infection is found, more tests will usually be performed to see if the bladder, ureters, urethra and kidneys are infected as well. Usually, the first test done will be an ultrasound.
Another way is to dip test strips in the urine and these will show if a urine infection is present. However, these are usually not enough to be sure, unless the child has had infections before. The test strip results may be normal even if a child has an infection. Collecting clean urine for this test from young children can be difficult and a special bag may be used. Sometimes the urine is collected in other ways, such as using a catheter. If a urine infection is found, more tests will usually be performed to see if the bladder, ureters, urethra and kidneys are infected as well. Usually, the first test done will be an ultrasound.
 Cystitis is a bacterial infection that causes your bladder to become inflamed. It happens when bacteria enter your bladder through your urethra, the tube that carries urine out of your body.
Cystitis is a bacterial infection that causes your bladder to become inflamed. It happens when bacteria enter your bladder through your urethra, the tube that carries urine out of your body. To find out if you have a UTI, your doctor will need to test a clean sample of your urine. The doctor or nurse will give you a clean plastic cup and a special wipe. Wash your hands before opening the cup. When you open the cup, don’t touch the inside of the lid or the inside of the cup. Put the cup in easy reach. Separate the labia, the outer lips of the vagina, with one hand and with your other hand, clean the genital area with the wipe. Wipe from front to back and do not touch or wipe the anus. While still holding the labia open, pass a little bit of urine into the toilet. Then, catch the rest in the cup. This is called a “clean-catch” sample. Let the rest of the urine fall regularly into the toilet.
To find out if you have a UTI, your doctor will need to test a clean sample of your urine. The doctor or nurse will give you a clean plastic cup and a special wipe. Wash your hands before opening the cup. When you open the cup, don’t touch the inside of the lid or the inside of the cup. Put the cup in easy reach. Separate the labia, the outer lips of the vagina, with one hand and with your other hand, clean the genital area with the wipe. Wipe from front to back and do not touch or wipe the anus. While still holding the labia open, pass a little bit of urine into the toilet. Then, catch the rest in the cup. This is called a “clean-catch” sample. Let the rest of the urine fall regularly into the toilet.