
The Causes and Treatment of a UTI
Acute cystitis or bladder infection, commonly known as urinary tract infection, affects parts of the urinary tract. The urinary system, also known as the renal system, consists of the urethra, bladder, ureters and kidneys. These organs produce, collect and eliminate urine from the body. When infected, it can cause a bladder infection and in severe cases, a kidney infection.
When the urinary tract gets infected, the following are the three types of infection that can occur.
 Cystitis is a bacterial infection that causes your bladder to become inflamed. It happens when bacteria enter your bladder through your urethra, the tube that carries urine out of your body.
Cystitis is a bacterial infection that causes your bladder to become inflamed. It happens when bacteria enter your bladder through your urethra, the tube that carries urine out of your body.- Urethritis is inflammation of the urethra. Pain when urinating is the main symptom of urethritis.
- Pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the kidney tissue, calyces, and renal pelvis. It is commonly caused by bacterial infection that has spread up the urinary tract or travelled through the bloodstream to the kidneys.
Symptoms of UTIs
These are the symptoms one should look out for:
- wanting to urinate more often and urgently, if only a few drops
- burning pain or a scalding sensation when urinating
- a feeling that the bladder is still full after urinating
- pain above the pubic bone
- blood in the urine
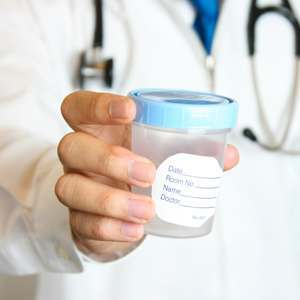 To find out if you have a UTI, your doctor will need to test a clean sample of your urine. The doctor or nurse will give you a clean plastic cup and a special wipe. Wash your hands before opening the cup. When you open the cup, don’t touch the inside of the lid or the inside of the cup. Put the cup in easy reach. Separate the labia, the outer lips of the vagina, with one hand and with your other hand, clean the genital area with the wipe. Wipe from front to back and do not touch or wipe the anus. While still holding the labia open, pass a little bit of urine into the toilet. Then, catch the rest in the cup. This is called a “clean-catch” sample. Let the rest of the urine fall regularly into the toilet.
To find out if you have a UTI, your doctor will need to test a clean sample of your urine. The doctor or nurse will give you a clean plastic cup and a special wipe. Wash your hands before opening the cup. When you open the cup, don’t touch the inside of the lid or the inside of the cup. Put the cup in easy reach. Separate the labia, the outer lips of the vagina, with one hand and with your other hand, clean the genital area with the wipe. Wipe from front to back and do not touch or wipe the anus. While still holding the labia open, pass a little bit of urine into the toilet. Then, catch the rest in the cup. This is called a “clean-catch” sample. Let the rest of the urine fall regularly into the toilet.
If you are prone to UTIs, your doctor may want to x-ray or ultrasound your urinary tract. These can help show swelling, stones, or blockage. Your doctor also may want to look inside your bladder using a cystoscope, which is a small tube that’s put into the urethra to see inside of it and the bladder.
Treatment
Often, symptoms clear up within a few days of treatment. You may need to continue antibiotics for a week or more and be sure to take the entire course of antibiotics, as prescribed. For an uncomplicated UTI that occurs when you’re otherwise healthy, your doctor may recommend a shorter course of treatment, such as taking an antibiotic for one to three days. Whether this short course of treatment is enough to treat your infection depends on your particular symptoms and medical history. It is advisable that one consults a doctor when in discomfort to prevent an infection from worsening or spreading.
TOP 5
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONTreatments |
|||||
| UTI Clear | Urizol | Native Remedies UTI-Clear | Nutrition Depot Urinary Tract Support | Pure Encapsulations Cranberry NS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Price (1 bottle) Price (6 bottles) Best Value |
$49.95 $139.80 |
$47.95 $287.70 |
$29.95 $179.70 |
$30.00 $180.00 |
$27.00 $162.00 |
| Overall Rating | 99.30% | 77.0% | 72.50% | 63.20% | 61.50% |
| Effectiveness |





|





|





|





|





|
| Speed of Results | Extremely Fast | Good | Average | Slow | Slow |
| Quality of Ingredients | Premium | Good | Average | Average | Average |
| Customer Satisfaction Evaluation | 99.40% | 76.50% | 74.20% | 67.10% | 60.5% |
| Safety Evaluation | Safe for Use | Safe for Use | Safe for Use | Safe for Use | Safe for Use |
| Customer Service Rating |





|





|





|





|





|
| Reorder Rate | Highest | Good | Good | Average | Average |
| Return Policy | Risk Free | Risk Free | Good | Unopened & Restocking Fee | 30 Days + Fee |
| Success Rate | 99.60% | 78.30% | 74% | 71.10% | 68.50% |

 Subscribe Now
Subscribe Now











